Network security has become a top priority for organizations and individuals in today’s interconnected world. With the increasing number of devices connected to the internet, the risk of cyber-attacks has also increased.
Cyber-attacks can be devastating, resulting in data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
In this article, we will discuss the top 10 types of attacks in network security, their characteristics, and prevention measures.
List of Top 10 Types Of Attacks In Network Security

Here is the List of Top 10 Types Of Attacks In Network Security:
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a type of social engineering given that an attacker sends an e-mail or message that looks like it was sent by someone well-known.
The idea of phishing attacks is to gain the user’s trust and get him or her to surrender the needed data like a password, credit card number or personal profile.
Some of the most common attacks are phishing attacks which can be made through email, phone calls, text messages, etc.
2. Malware Attacks
Malware is therefore a kind of program developed to execute malicious activities on a computer system. And it could be viruses, worms, Trojan horses ransomware etc.
A malware attack has the potential of inflicting damage on the network such as leakage of data, system failure, and money loss.
3. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
By overloading a single network or host with traffic from many sources, DoS attacks are designed to prevent a system from answering requests of the user.
This can be done with the help of botnets, that is networks of infected computers. No special training is needed to mount a DoS attack, and the attack can seriously impair a network during its execution.

4. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
MitM attacks involve an attacker eavesdropping on information exchanged between two parties. This can be achieved by compromising a common public Wi-Fi connection or by using bogus SSL certificates.
Plenty of original information can be intercepted, such as a password or credit card number.
5. SQL Injection Attacks
An example of an injection is the SQL attack in which a malicious script is added to a database with the goal of acquiring sensitive data. This can be achieved by taking advantage of a weakness in web applications and subverting SQL-based databases.
Due to their flexibility, SQL injection attacks can cause great harm to a network, for instance, by exposing data or making the systems crash.
6. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
A cross-site scripting enables an attacker to embed a piece of code into a web application that develops the purpose of capturing and devouring as much sensitive information as possible.
This can be achieved through the weaknesses in the web application that utilizes JavaScript. XSS attacks have the potential to compromise a network by stealing and exposing data or causing it to fail.
7. Brute Force Attacks
Hacking is an attempt of forceful entry by trying to guess a password or an encryption key through guessing. It means brute force attacks can be performed for any network or system and such attacks can be dangerous if the attacker gains access.
8. Sniffing Attacks
Sniffing attacks are used in the context of getting hold of the passing data by intercepting the network traffic. This can be done with the help of packet sniffers, as well as with unauthorized access to network devices.
While sniffing attacks the common goal is to get passwords, credit card numbers, or other excessive information.
9. Spoofing Attacks
Spoofing attacks emulate valid working devices or users in an attempt to obtain access to a network that one is not supposed to upon. Spoofing attacks can be targeted at any network or system, and those with success can be greatly damaging.
10. Zero-Day Exploits
They are used to take advantage of some flaws in software as well as in the hardware that are unknown to the vendor. Zero-day attacks can be directed at any network or system, and if they are successful the consequences can be severe.
Top 7 Best Practices for Network Security
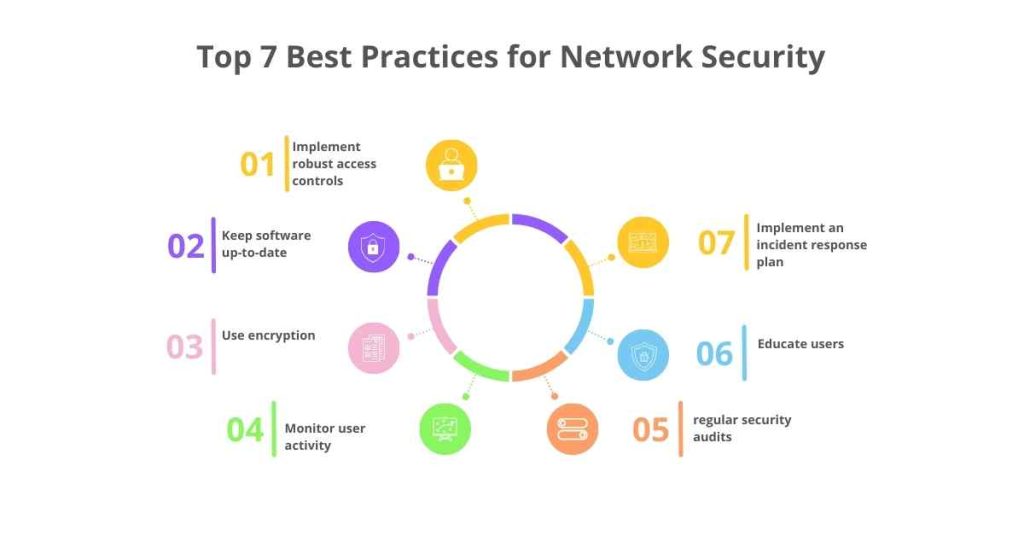
By following these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of network security attacks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their systems and data.
1. Implement robust access controls
Strong passwords should be used, and two-factor authentication should lead to regular reviews of the users with access to the systems and data.
2. Keep software up-to-date
Always remember to patch or update your operating systems to close exploit vectors.
3. Use encryption
Secure data that is being transferred or stored by applications, services, processes, and devices from unauthorized usage.
4. Monitor user activity
Employ IDS and Security analytics to track user activity and look out for instances where there is any odd activity detected.
5. regular security audits
Perform security scans often that is, for a security risk assessment of the organization and to review the efficiency of security measures.
6. Educate users
Teach your users about what security threats are, and how to deal with specific threats like phishing or social engineering.
7. Implement an incident response plan
Create an incident response plan and use this to perform a quick and efficient response where there has been a security breach.
Summary
Here is the summary for the blog title Top 10 Types of Attacks in Network Security.
- Phishing Attacks
- Malware Attacks
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
- SQL Injection Attacks
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Attacks
- Brute Force Attacks
- Sniffing Attacks
- Spoofing Attacks
- Zero-Day Exploits
Conclusion
In conclusion, network security is a pressing concern that requires a multifaceted approach to address. By understanding the top 10 types of attacks in network security, organizations can take proactive measures to prevent or mitigate their impact.
Educating users, implementing robust security controls, and conducting regular security audits are essential steps to protecting against these types of attacks.
FAQs: Top 10 Types of Attacks in Network Security
1. What are the most common types of network security attacks?
Ans: The most common types of network security attacks include phishing attacks, malware attacks, man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, denial of service (DoS) attacks, SQL injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, social engineering attacks, zero-day exploits, insider threats, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
2. How can I protect my organization from phishing attacks?
Ans: To protect your organization from phishing attacks, educate your users on how to identify phishing attempts, use two-factor authentication, and implement email filtering to detect and block suspicious emails.
3. What is the difference between a virus and malware?
Ans: A virus is a malware that replicates itself by infecting other files or systems. Malware, on the other hand, is a broader term that refers to any type of software designed to harm or exploit a computer system. Malware can include viruses, Trojans, spyware, and ransomware.
4. How can I prevent insider threats?
Ans: To prevent insider threats, implement access controls, monitor user activity, and conduct regular security audits to detect and respond to suspicious behaviour.
5. What is the purpose of a firewall in network security?
Ans: A firewall is designed to prevent unauthorized access to a computer system or network by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined security rules.
6. Can I use antivirus software to protect my organization from all types of malware?
Ans: No, antivirus software is not effective against all types of malware. While antivirus software can detect and remove viruses, Trojans, and other types of malware, it may not detect newer or more sophisticated malware. A layered security approach is recommended to protect against all types of malware.
7. How can I protect my organization from denial of service (DoS) attacks?
Ans: To protect your organization from DoS attacks, use firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and failover systems to detect and respond to DoS attacks.
8. What is the difference between a password and two-factor authentication?
Ans: A password is a single authentication factor that is used to verify a user’s identity. Two-factor authentication, on the other hand, requires two separate authentication factors, such as a password and a fingerprint or a smart card, to verify a user’s identity.
9. How often should I conduct security audits?
Ans: Security audits should be conducted regularly to ensure the effectiveness of security controls and identify vulnerabilities in systems and networks. The frequency of security audits will depend on the size and complexity of the organization, as well as regulatory requirements.
10. What should I do in the event of a security breach?
Ans: In the event of a security breach, respond quickly and effectively by following established incident response procedures. This may involve containing the breach, eradicating malware or other threats, restoring systems and data from backups, and notifying affected parties.