Phishing Simulations
Phishing Is A Serious Threat To Businesses
Social engineering poses a significant risk to businesses, with phishing being a common tactic.

What Is A Phishing Simulation Service?
At CyberSapiens, we provide a phishing simulation service which is a phishing test that is designed to improve awareness of phishing scams across your organization.
With a phishing test, simulated phishing emails are sent to staff across your organization. The emails act like real phishing emails to get your employees to click links, enter passwords or perform other actions often requested by phishing emails. The purpose of the test is that staff can make mistakes and fall for simulated phishing emails and learn from their mistakes in a safe environment without the drastic consequences of a real phishing scam.
Conduct Authorized Phishing Attacks to test and re-test your employees susceptibility to Social Engineering attacks!
In today’s environment, social engineering attacks are prevalent and increasing. The human element is often the weakest component in a company’s security. Attackers know this and exploit it. 47% of cyber security attacks such as social engineering, spear-phishing, and ransomware attacks are that are financially motivated.
It’s time to test your employees and make them proactive to identify and report phishing attacks.
Features & Benefits
- Multiple Phishing Emails and Scenarios to simulate
- Comprehensive and easy Reporting
- Easy to deliver simulation
- Customized templates for every industry sectors
- Unlimited simulations

Get In Touch
By filling this form ↓
FAQ's
Phishing simulation aims to educate and raise awareness among employees about the risks associated with phishing attacks and identify any vulnerabilities in the organization's security measures.
By simulating a phishing attack, phishing simulation can be used to test and improve an organization's security awareness.
Typically, phishing simulation entails sending a fake phishing email to employees that appear to be legitimate emails from a trusted source, such as a bank or a well-known company.
The email could include a link to a bogus login page where the employee is prompted to enter their login credentials.
Yes, phishing simulation can effectively raise security awareness in an organization and reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attacks.
Several studies have found that phishing simulation can raise employee awareness of the dangers of phishing attacks and improve their ability to detect and report such attacks.
Phishing simulation can also assist in identifying any flaws in an organization's security measures and provide an opportunity to address them before an attack occurs.
Organizations can reduce the likelihood of a successful phishing attack and the impact of any attacks that do occur by educating employees and testing their knowledge and skills.
Here are the following benefits of phishing simulation service:
Increased Security Awareness
Phishing simulation can help employees recognize the signs of a phishing attack and understand the risks involved. This increased awareness can help prevent successful attacks and minimize the impact of any attacks that do occur.
Improved Security Measures
Phishing simulation can help identify any vulnerabilities in an organization's security measures and allow them to be addressed before an attack occurs. This can help to improve overall security and lower the likelihood of successful attacks.
Improved incident Response
By practicing incident response procedures during phishing simulation exercises, organizations can better prepare for real-world attacks and respond to them more quickly and effectively when they occur.
A variety of organizations can carry out phishing simulations, including:
Internal IT Security Teams: Many organizations have IT security teams managing security measures, including phishing simulations.
Third-party Security Providers: Some businesses may outsource their security measures to third-party cybersecurity providers. These providers may provide phishing simulation services as part of their overall security package.
Security Consulting Firms: Security consulting firms can also offer phishing simulation services as part of their consulting services. These companies can advise businesses on improving their security measures and assist them in developing effective incident response plans.
Phishing simulations are used to assess a company's security awareness and susceptibility to phishing attacks.
Some of the main reasons why running phishing simulations can be beneficial are as follows:
Identify Flaws: Phishing simulations can assist in identifying flaws in an organization's security awareness, policies, and procedures.
Phishing simulations can be used to test the effectiveness of security controls such as email filters and anti-phishing training.
Employee Education: Phishing simulations can be used to teach employees how to recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
Reduce Risk: Phishing simulations can help reduce the risk of a successful phishing attack by identifying vulnerabilities and testing security controls.
Phishing simulations can be useful in raising awareness and educating people about the dangers of phishing attacks. Organizations can train their employees to recognise the warning signs of a phishing attempt and take appropriate action to prevent a successful attack by simulating a phishing attack.
However, the effectiveness of phishing simulations can be affected by a variety of factors, including simulation quality, frequency of training, and employee engagement. The simulation's effectiveness may be limited if it is poorly executed or if employees are not engaged in the training.
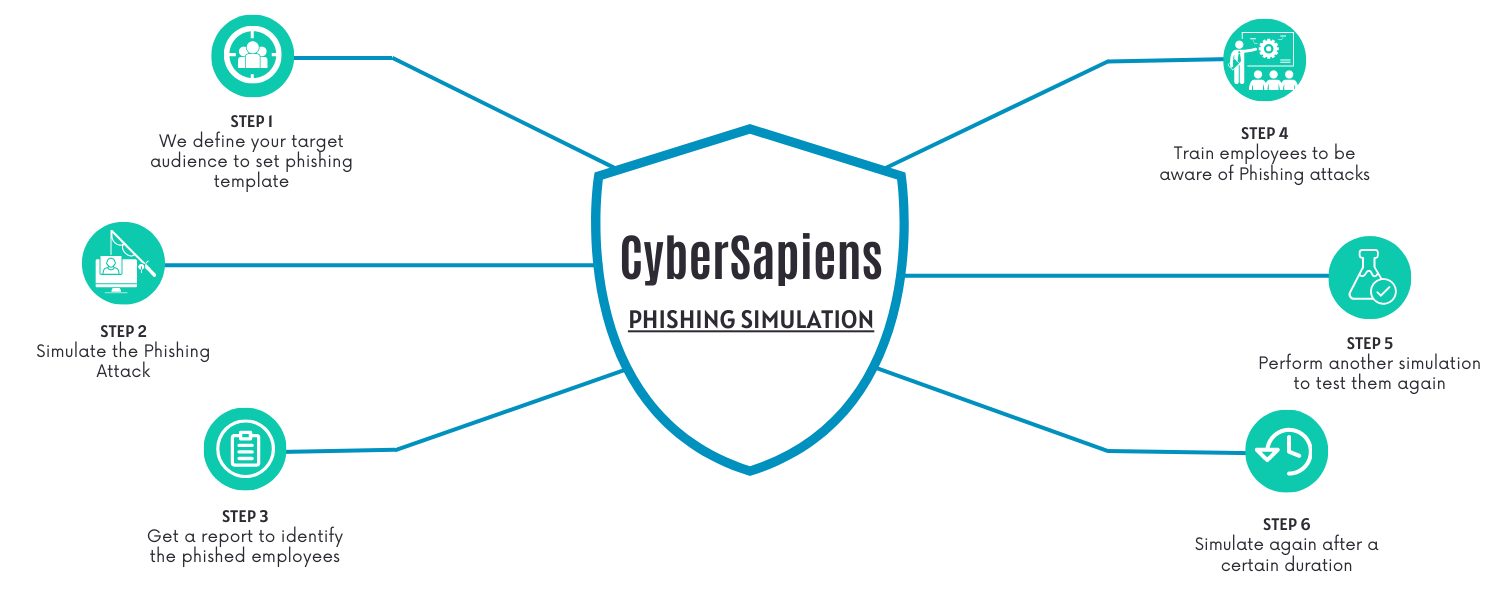
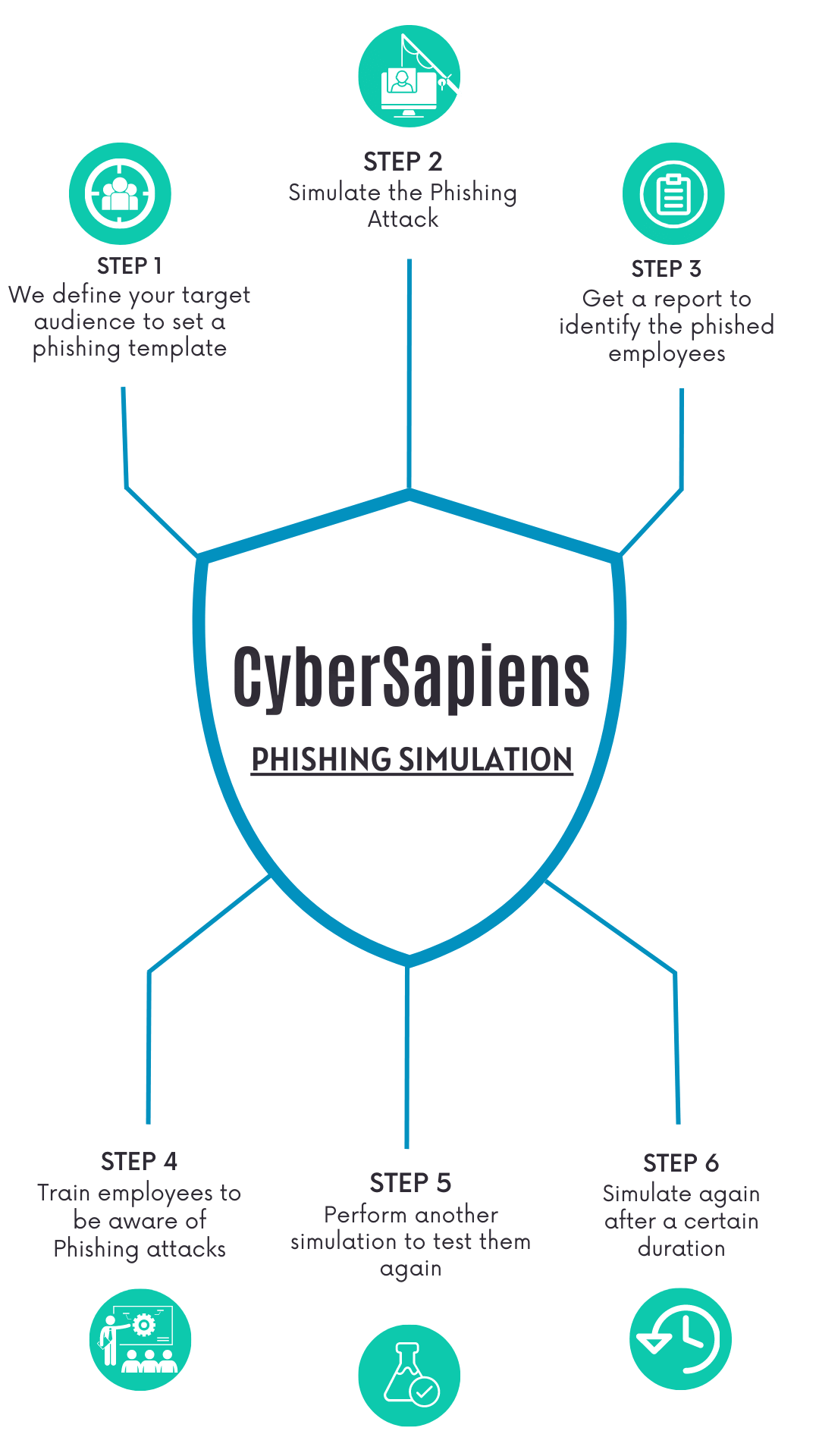
Our Phishing Simulation Methodology involves the following steps:
- Step 1: Define your target audience to set a phishing template
- Step 2: Simulate the Phishing Attack
- Step 3: Get a report to identify the phished employees
- Step 4: Train them to be aware of Phishing Attacks
- Step 5: Perform another simulation to test them again
- Step 6: Simulate again after a certain duration
The most common warning signs of phishing include:
Unexpected or Suspicious Emails: Phishing emails may appear from a legitimate source but often have suspicious elements, such as a strange or misspelled email address.
Urgent or Threatening Messages: Phishing emails may use scare tactics to get the recipient to click on a link or download an attachment, such as threatening to close an account.
Suspicious Links or Attachments: Phishing emails often contain links or attachments that, when clicked or downloaded, can infect the recipient's computer with malware.
Requests for Sensitive Information: Phishing emails often ask recipients to provide sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or credit card numbers.
Poor Spelling and Grammar: Many phishing emails contain poor spelling and grammar, which can signify that they need to be more legitimate.
Unusual Sender or Subject: Phishing emails may come from an unfamiliar sender or have a subject that needs to be clarified in context.
Suspicious URL: Phishing emails may contain links that, when hovered over, reveal a suspicious or unfamiliar URL.
There are several types of phishing, some of the most common include:
Email Phishing: This involves using email to trick users into providing sensitive information such as login credentials or personal data.
Smishing: This is a type of phishing that involves the use of text messages (SMS) to deceive users.
Vishing: This involves using voice calls or VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) to trick users into divulging sensitive information.
Spear Phishing: This is a targeted type aimed at specific individuals or organizations. Attackers use the information they have gathered about the target to make their phishing attempts more convincing.
Clone Phishing: This involves creating a fake website that looks similar to a legitimate website, intending to steal login credentials or personal information.
Whaling: This type of phishing is aimed at high-level executives or key individuals within an organization.
Social Media Phishing: This involves using social media platforms to deceive users into providing sensitive information.
Search Engine Phishing: This is a type of phishing where attackers create fake websites that appear in search results to steal personal information.
When a phishing email is opened, it can have various consequences depending on the intent of the attacker and the actions taken by the recipient. Some common scenarios include:
Installation of Malware: The email may contain a malicious attachment or a link to a fake website that, when clicked, installs malware on the recipient's device. The malware can then be used to steal sensitive data, track keystrokes, or take control of the device.
Credential Theft: The email may prompt the recipient to enter their login credentials on a fake website or provide sensitive information such as credit card details or social security numbers. The attacker can then use this information to gain unauthorized access to the victim's accounts or commit identity theft.
To avoid failing a phishing test, adhere to the following best practices:
Be Aware of Unexpected Emails: Be wary of emails from unknown senders, especially those that request personal or sensitive information or contain time-sensitive requests.
Examine the Sender's Email Address: Scammers frequently use email addresses that resemble legitimate addresses but have minor differences. Before responding to an email, always check the sender's email address.
Check the Email's Content: Look for misspellings, poor grammar, and suspicious links or attachments.
Avoid Clicking on Suspicious Links: Hover over links to see the URL before clicking, and never enter sensitive information on an unfamiliar website.
The average phishing rate is calculated by dividing the total number of phishing attempts by the number of successful phishing attempts and multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage. The average phish rate is calculated as follows:
(Number of Successful Phishing Attempts / Total Number of Phishing Attempts) x 100% = Average Phish Rate
For example, if a company sends out 100 simulated phishing emails and 10 employees fall for one of them, the average phishing rate would be:
(10 / 100) x 100% = 10%
This means that the fake phishing email duped 10% of the employees. The average phishing rate can be used to track the efficacy of security awareness training and phishing simulations.