As technology advances, the importance of network security has become increasingly significant. One crucial aspect of maintaining a secure network is Open Policy Service (OPS).
OPS plays a vital role in network security by allowing administrators to create and enforce policies that govern network access, usage, and traffic. In this article, we will delve into the topic “What is OPS in Network Security?” world of OPS, exploring its meaning, functions, benefits, and importance in network security.
What is OPS?
Open Policy Service (OPS) is a network protocol that allows administrators to create, manage, and enforce policies on a network. Policies, in this context, refer to a set of rules that govern network access, usage, and traffic.
OPS enables administrators to create policies that define who can access the network, what resources they can access, and how they can use those resources. OPS is an open-standard protocol, which means that it can be implemented on various network devices, platforms, and operating systems.
History of OPS
The Open Policy Service (OPS) protocol was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in the late 1990s. The IETF is a non-profit organization that aims to develop standardized networking protocols and technologies. OPS was designed to address the growing need for network security and management.
At the time, network administrators were using proprietary protocols and technologies to manage their networks, which led to compatibility issues and high costs.
How OPS Works?
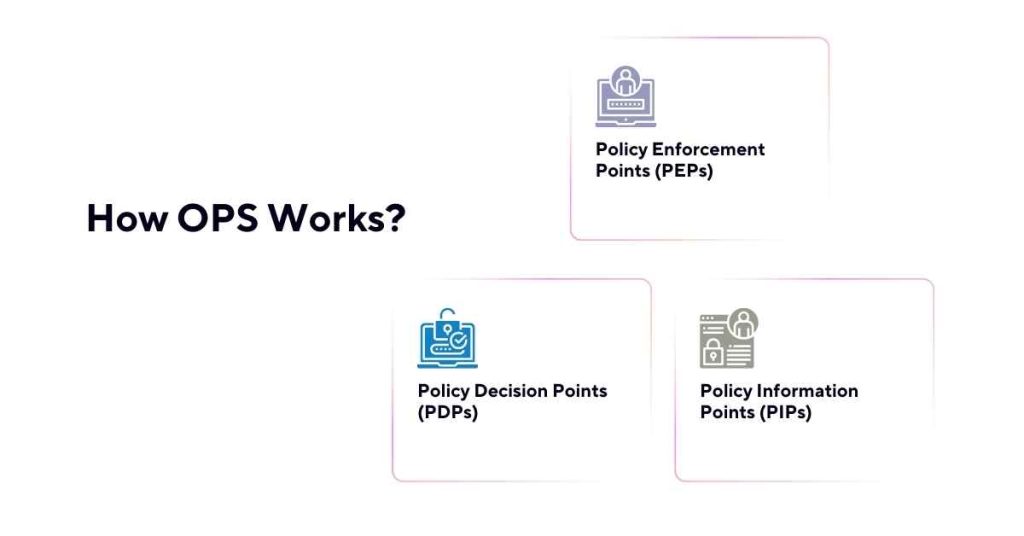
OPS works by using three main components: Policy Decision Points (PDPs), Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs), and Policy Information Points (PIPs).
1. Policy Decision Points (PDPs)
PDPs are responsible for making policy decisions based on the policies created by administrators. PDPs receive policy requests from PEPs and use the policies to determine whether the request should be granted or denied.
2. Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs)
PEPs are responsible for enforcing policies on the network. PEPs receive policy decisions from PDPs and implement them on the network.
3. Policy Information Points (PIPs)
PIPs are responsible for providing information to PDPs. PIPs collect information about network devices, users, and resources, which is used by PDPs to make policy decisions.
Top 4 Functions of OPS

OPS performs several functions that enable network administrators to create and enforce policies on a network.
1. Policy Management
OPS allows administrators to create, manage, and update policies on a network.
2. Policy Distribution
OPS enables the distribution of policies to PEPs on the network.
3. Policy Decision
OPS enables PDPs to make policy decisions based on the policies created by administrators.
4. Policy Enforcement
OPS enables PEPs to enforce policies on the network.
Top 4 Benefits of OPS
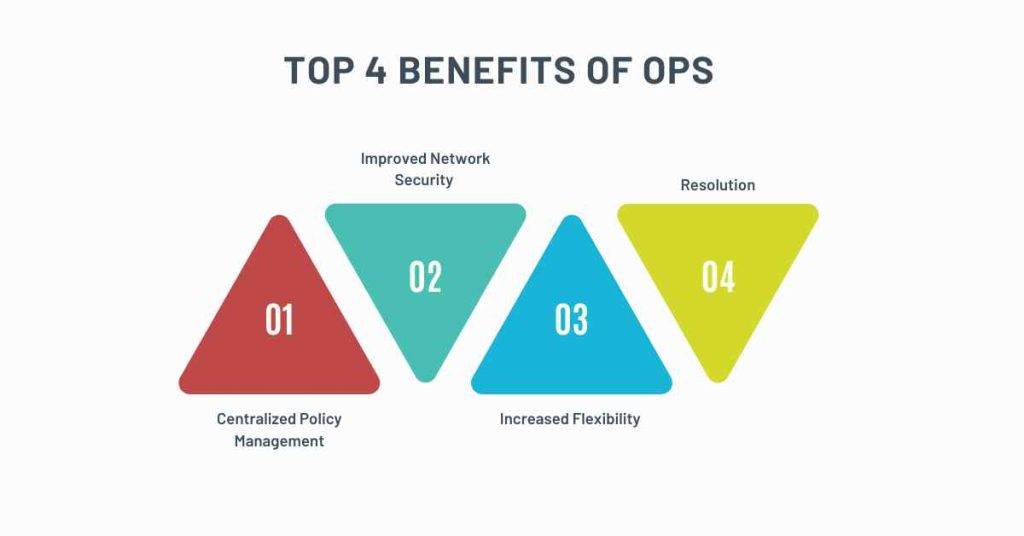
OPS provides several benefits that enhance network security and management.
1. Centralized Policy Management
OPS enables administrators to create and manage policies from a central location, making it easier to manage the network.
2. Improved Network Security
OPS enables administrators to create policies that define network access and usage, improving network security.
3. Increased Flexibility
OPS allows administrators to create policies that can be applied to various network devices and platforms.
4. Reduced Costs
OPS enables administrators to manage policies from a central location, reducing the costs associated with managing network policies.
Importance of OPS in Network Security
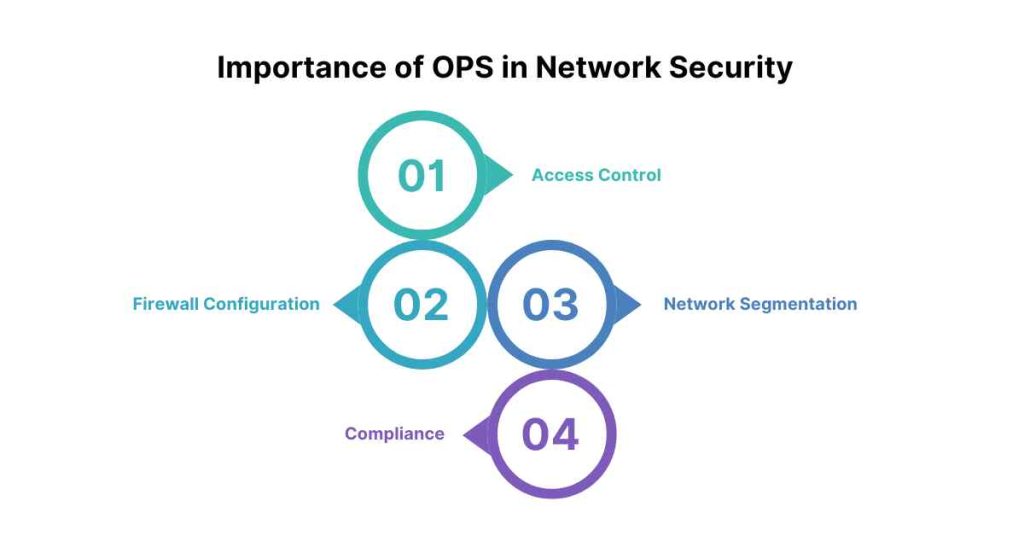
OPS plays a crucial role in network security by allowing administrators to create and enforce policies that govern network access, usage, and traffic. OPS is essential in several aspects of network security:
1. Access Control
OPS enables administrators to create policies that define who can access the network and what resources they can access.
2. Firewall Configuration
OPS enables administrators to create policies that define the rules and exceptions for firewall configuration.
3. Network Segmentation
OPS enables administrators to create policies that define network segmentation, which isolates sensitive data and systems.
4. Compliance
OPS helps administrators demonstrate compliance with various regulations and standards, such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA.
Challenges and Limitations of OPS
While OPS is an essential tool in network security, it is not without its challenges and limitations.
1. Complexity
OPS can be complex to implement and manage, requiring specialized skills and knowledge.
2. Scalability
OPS may not scale well to large and complex networks, requiring multiple policies and configurations.
3. Interoperability
OPS may not be compatible with all network devices and platforms, requiring additional configuration and management.
4. Security Risks
OPS may introduce security risks if not implemented and managed correctly, such as unauthorized access to network resources.
Best Practices for Implementing OPS
To overcome the challenges and limitations of OPS, administrators should follow best practices when implementing and managing OPS.
1. Develop a clear understanding of OPS
Administrators should understand the basics of OPS and its components, including PDPs, PEPs, and PIPs.
2. Develop a policy management strategy
Administrators should develop a policy management strategy that outlines the policies, procedures, and practices for managing OPS.
3. Test and validate policies
Administrators should test and validate policies before implementing them on the network.
4. Continuously monitor and evaluate policies
Administrators should continuously monitor and evaluate policies to ensure that they are effective and up-to-date.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Open Policy Service (OPS) is a network protocol that plays a crucial role in network security by allowing administrators to create and enforce policies that govern network access, usage, and traffic. OPS provides several benefits, including centralized policy management, improved network security, increased flexibility, and reduced costs.
However, OPS also has its challenges and limitations, requiring administrators to follow best practices when implementing and managing OPS. As network security continues to evolve, OPS remains an essential tool in maintaining a secure and compliant network.
FAQs: What is OPS in Network Security?
1. What is Open Policy Service (OPS)?
Ans: Open Policy Service (OPS) is a network protocol that allows administrators to create, manage, and enforce policies on a network. Policies, in this context, refer to a set of rules that govern network access, usage, and traffic.
2. How does OPS work?
Ans: OPS works by using three main components: Policy Decision Points (PDPs), Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs), and Policy Information Points (PIPs). PDPs make policy decisions based on policies created by administrators, PEPs enforce policies on the network, and PIPs provide information to PDPs.
3. What are the benefits of using OPS?
Ans: The benefits of using OPS include centralized policy management, improved network security, increased flexibility, and reduced costs. OPS enables administrators to create and manage policies from a central location, improving network security and reducing the costs associated with managing network policies.
4. What is the main difference between OPS and other policy management solutions?
Ans: The main difference between OPS and other policy management solutions is its open-standard protocol, which means that it can be implemented on various network devices, platforms, and operating systems. This makes OPS a more flexible and adaptable solution for network policy management.
5. Can OPS be used on all types of networks?
Ans: Yes, OPS can be used on various types of networks, including wireless networks, wired networks, and virtual private networks (VPNs). OPS is a protocol that can be implemented on different devices, platforms, and operating systems.
6. How secure is OPS?
Ans: OPS is a secure protocol that enables administrators to create and enforce policies that govern network access, usage, and traffic. OPS uses encryption and authentication to ensure that policies are transmitted and enforced securely.
7. Can OPS be used to manage user access to network resources?
Ans: Yes, OPS can be used to manage user access to network resources. Administrators can create policies that define who can access the network, what resources they can access, and how they can use those resources.
8. How do I get started with implementing OPS on my network?
Ans: To get started with implementing OPS on your network, you should first develop a clear understanding of OPS and its components, including PDPs, PEPs, and PIPs. You should also develop a policy management strategy that outlines the policies, procedures, and practices for managing OPS.
9. Can OPS be integrated with other security tools and technologies?
Ans: Yes, OPS can be integrated with other security tools and technologies, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). OPS can also be integrated with network management systems (NMS) and other security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
10. What are some common applications of OPS in network security?
Ans: OPS is commonly used in network security to manage access control, firewall configuration, network segmentation, and compliance with various regulations and standards, such as PCI-DSS and HIPAA. OPS is also used to manage user access to network resources and to enforce policies on the network.