The transportation and logistics industry has significantly transformed in recent years, with the increasing use of digital technologies and connected devices.
While these advancements have improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experience, they have also introduced new cybersecurity risks. The need for robust cyber security measures has become paramount as the industry becomes more interconnected.
A cyber security audit is crucial in identifying vulnerabilities and implementing measures to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
In this article, we will explore the importance of cyber security audit for transportation and logistics industry, the key areas to focus on, and provide actionable tips for implementing a successful audit.
Why Cyber Security Audits are Essential for Transportation and Logistics?

The transportation and logistics industry handles vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer information, payment details, and shipping schedules. A cyber security breach can result in significant losses, damage to reputation, and regulatory penalties.
Some of the key reasons why cyber security audits are essential for the transportation and logistics industry include:
1. Protection of sensitive data
A cyber security audit works to observe risks and openings that can be exploited by cyber-attackers in order to reach sensitive information and data.
2. Regulatory compliance
Certain laws and regulations apply to transportation and logistics firms these are GDPR, HIPAA and TSA regulations. Compliance with these regulations is however achievable via a cyber security audit.
3. Prevention of supply chain disruptions
From the cyber security breakdowns, it is evident that they lead to disruption of the supply chain which leads to delays and loss in revenue. A cyber security audit assesses risk in the supply chain and allows organisations to put protection measures in place to reduce the possibility of interruption.
4. Protection of intellectual property
The transportation and logistics firms therefore have hard and soft assets in the form of intellectual property such as application software and business methods. Such intellectual property is safeguarded from cyber threats by undertaking a cyber security audit.
Key Areas to Focus on in a Cyber Security Audit
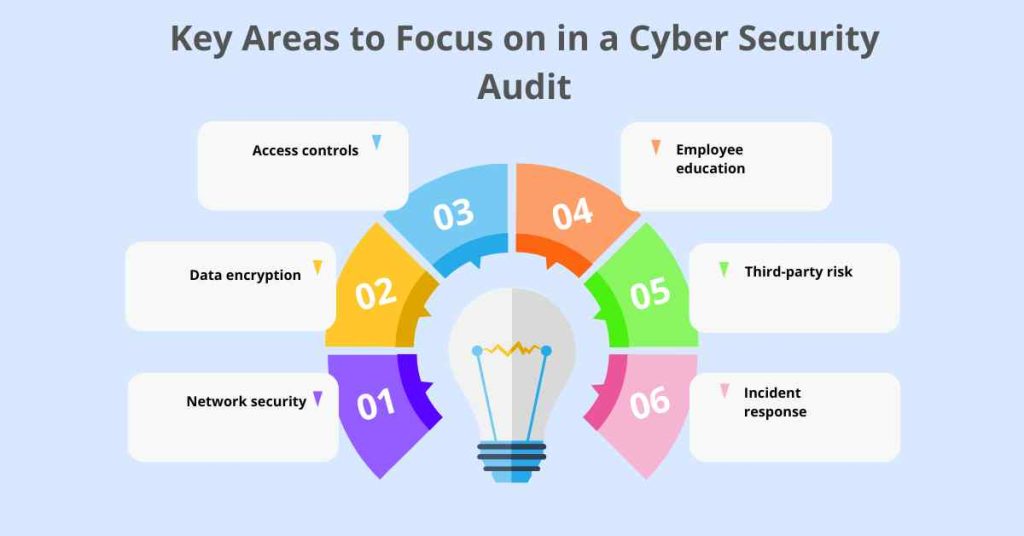
When conducting a cyber security audit in the transportation and logistics industry, there are several key areas to focus on. These include:
1. Network security
Determine the measures security measures currently in place such as firewalls, IDS and number and type of access.
2. Data encryption
Discuss the methods of data encryption about the encryption of data that is stored and that in motion.
3. Access controls
Discuss passwords, multi-factor authentication, and least privilege of access controls.
Software updates: Consider retrospective the frequency and utilization of software updates, and address of patch and vulnerability.
4. Employee education
Determine how much employees know about cyber security measures, how to avoid getting caught in phishing scams and what to do if they get compromised.

5. Third-party risk
Few organizations conduct regular evaluations of third-party vendors and suppliers, transportation companies, logistic companies etc.
6. Incident response
Discuss the company’s incident response plan and guidelines regarding communication, containment, and mitigation.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Successful Cyber Security Audit
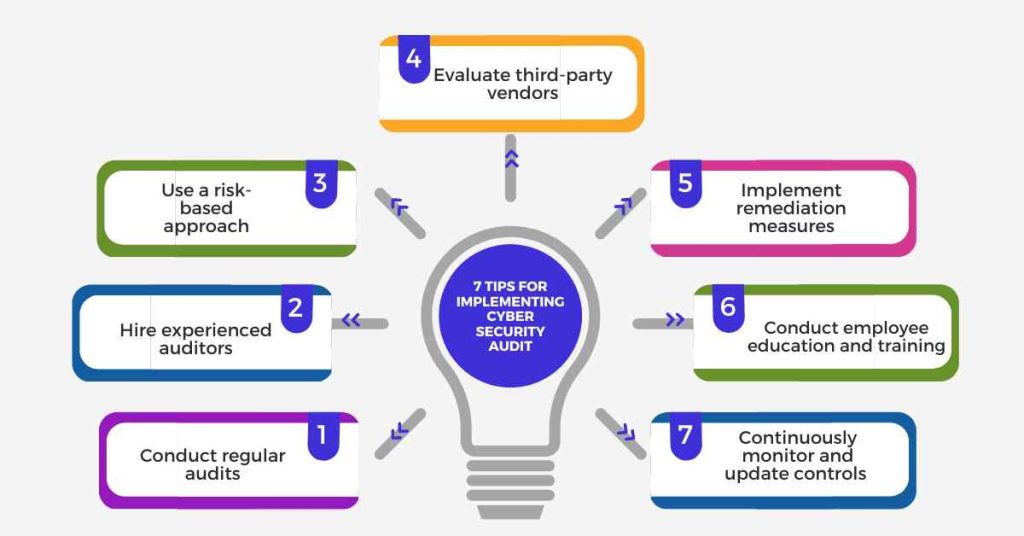
Implementing a successful cyber security audit in the transportation and logistics industry requires careful planning and execution. Here are some actionable tips to consider:
1. Conduct regular audits
Schedule a comprehensive cyber security audit, preferably at least an annual, to check that the company is not vulnerable.
2. Hire experienced auditors
Use professional personnel who have worked for at least three years in audit and who possess an understanding of cyber security and transportation and logistics.
3. Use a risk-based approach
This is important as it will ensure that the assessment follows the risk appetite of the organization identifying the important areas to use limited resources in tackling vulnerabilities.
4. Evaluate third-party vendors
Assess the security of third parties such as transportation services providers, logistic companies and so on.
5. Implement remediation measures
Conduct remedial action to these vulnerabilities such as operational patch management and remediating vulnerabilities.
6. Conduct employee education and training
Offer frequent tuition to workers as well as team-developed workshops that focus on practising cyber security measures with pipeline personnel.
7. Continuously monitor and update controls
Monitor proactively and maintain and adjust the existing controls which are the firewalls, virus and intrusion checking, access control systems and others.
Implementing a Cyber Security Audit in the Transportation and Logistics Industry
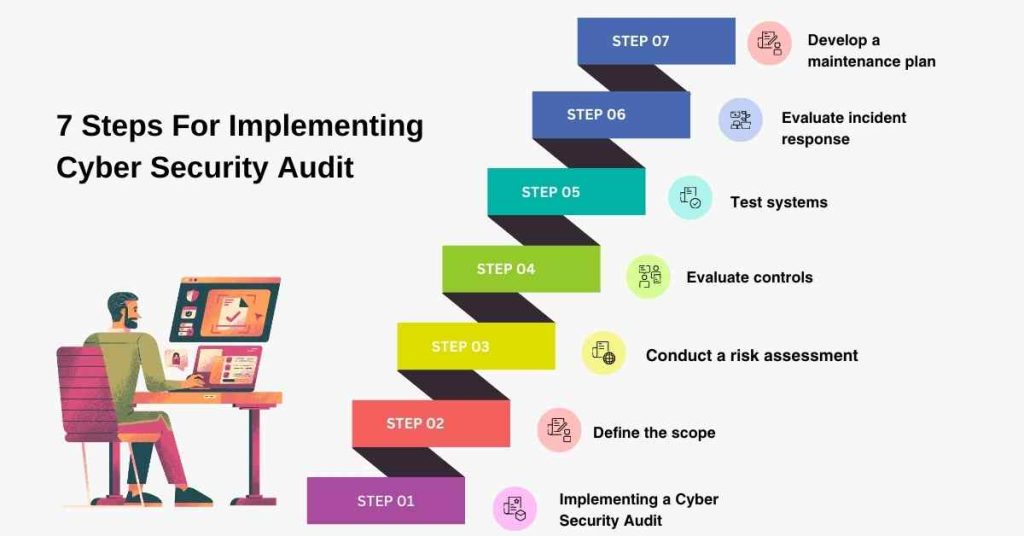
Implementing a cyber security audit in the transportation and logistics industry requires careful planning and execution. Here are some steps to consider:
1. Define the scope
Determine which areas of the process need to be audited and what goals need to be met in the course of the audit.
2. Conduct a risk assessment
A risk management evaluation should therefore be done, with a view to evaluating the degree of exposure to risks within the business.
3. Evaluate controls
Another set of metrics would be to assess the security controls such as the access control mechanisms, data encryption, and the ability to respond to a security incident if one were to occur.
4. Test systems
Responsible for performing tests on network, server and application to uncover inherent weaknesses.
5. Evaluate incident response
the company’s best-practice formal or informal plans and protocols for reporting, separation, and resolution measures of an incident occurrence.
6. Remediate vulnerabilities
Security remediation, for instance, patch management and vulnerability remediation.
7. Develop a maintenance plan
Maintenance should be developed with the frequency of monitoring and updating the control plan.
Conclusion
The transportation and logistics industry is increasingly dependent on digital technologies, introducing new cyber security risks. A cyber security audit is essential in identifying vulnerabilities and implementing measures to protect sensitive data and maintain compliance.
By focusing on key areas, including network security, data encryption, and access controls, and implementing remediation measures, companies can ensure the security of their data and protect their reputation.
Implementing a cyber security audit requires careful planning and execution, but the benefits are clear: protection of sensitive data, compliance with regulations, and reduction of supply chain disruptions.
FAQs: Cyber Security Audit for Transportation and Logistics
1. What is a cyber security audit?
Ans: A cyber security audit is an independent evaluation of an organization’s cyber security posture, including network security, data encryption, and access controls. It is designed to identify vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for improvement.
2. Why is cyber security important for transportation and logistics companies?
Ans: Cyber security is essential for transportation and logistics companies as they handle sensitive data, including customer information, payment details, and shipping schedules. A cyber security breach can result in significant losses, damage to reputation, and regulatory penalties.
3. What areas should be focused on in a cyber security audit?
Key areas to focus on include network security, data encryption, access controls, and incident response. These areas are critical in protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance.
4. Who should conduct a cyber security audit?
Ans: Cyber security audits should be conducted by experienced auditors with expertise in cyber security and the transportation and logistics industry. This ensures that the audit is thorough and relevant to the company’s specific needs.
5. How often should cyber security audits be conducted?
Ans: Cyber security audits should be conducted at least annually to ensure that the company’s security posture remains up-to-date. However, this may vary depending on the company’s size, industry, and risk profile.
6. What are the benefits of conducting a cyber security audit?
Ans: The benefits of conducting a cyber security audit include protection of sensitive data, compliance with regulations, reduction of supply chain disruptions, and protection of intellectual property.
7. How does a cyber security audit differ from a penetration test?
Ans: A cyber security audit is a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s cyber security posture, while a penetration test is a simulation of a cyber attack to test the organization’s defences. Both are important, but they serve different purposes.
8. Can a cyber security audit be conducted in-house?
Ans: While it is possible to conduct a cyber security audit in-house, it is recommended to engage an independent third-party auditor to ensure objectivity and expertise.
9. How long does a cyber security audit typically take?
Ans: The length of a cyber security audit can vary depending on the scope and complexity of the audit. Typically, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months to complete.
10. What should be done after a cyber security audit?
Ans: After a cyber security audit, the organisation should implement the recommended remediation measures, update policies and procedures, and provide employee education and training on cyber security best practices. The organization should also review and update its security controls to ensure ongoing protection.