This article aims to analyze the phenomenon of email impersonation attacks and establish their importance to the global population, specifically targeting individuals and organizations.
These are cases where the attackers electronically mail the victims’ organizations forging their identity with the view to eliciting sensitive information from the receivers or making them undertake some specific action.
In this article, we are going to give complete insight into how to defend against email impersonation attacks.
Understanding Email Impersonation Attacks
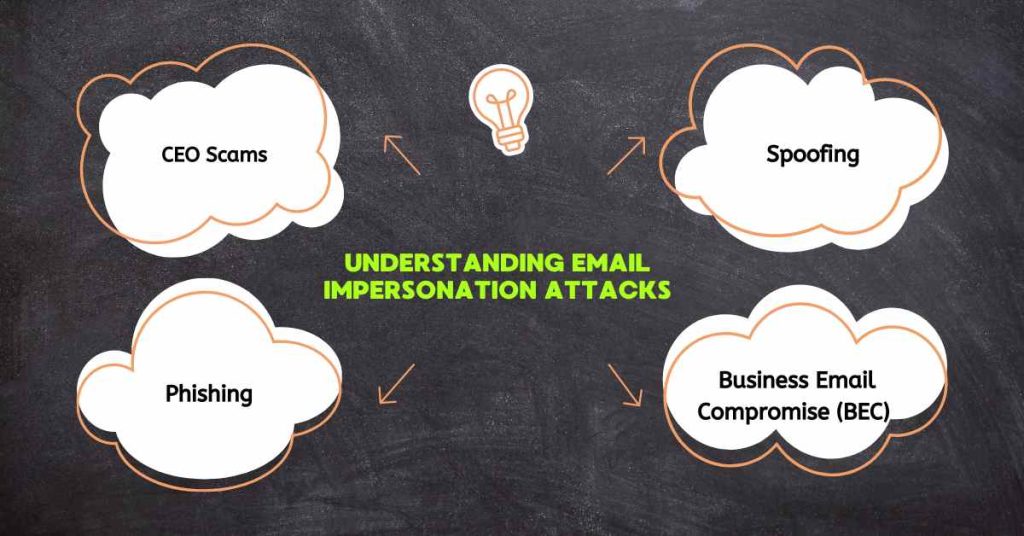
Before we dive into the defence strategies, it’s essential to understand how email impersonation attacks work. These attacks typically involve a combination of social engineering and technical tactics to deceive the recipient. Here are some common types of email impersonation attacks:
1. CEO Scams
Scammers impersonate a high-level executive, such as a CEO or CFO, and request sensitive information or money transfers from employees.
2. Phishing
Scammers send emails that appear to come from a legitimate source, such as a bank or online retailer, and ask the recipient to provide sensitive information or login credentials.

3. Spoofing
Scammers send emails that appear to come from a legitimate source but are sent from a fake email address.
4. Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Scammers impersonate a business partner or supplier and request money transfers or sensitive information.
Top 12 Ways to Defend Against Email Impersonation Attacks
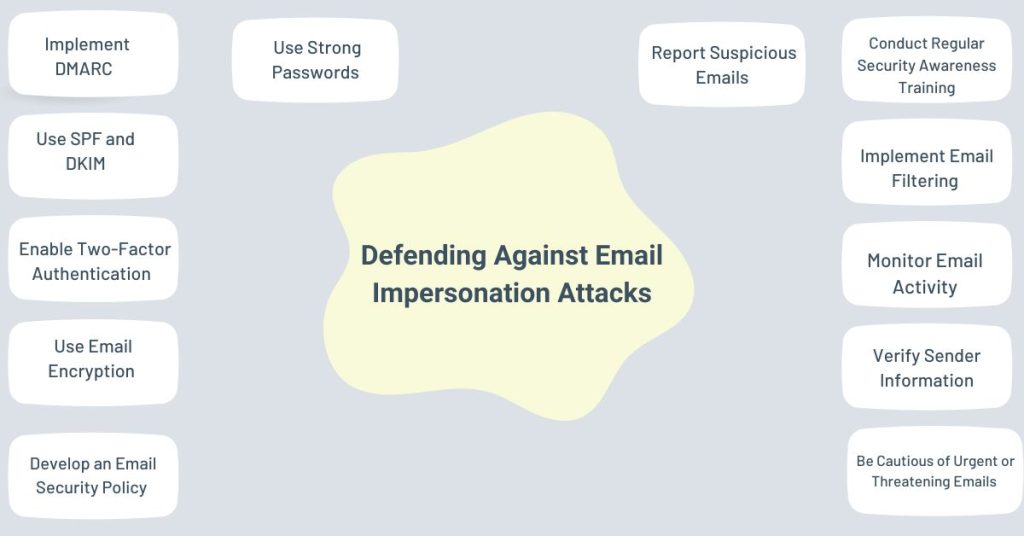
To defend against email impersonation attacks, individuals and organizations must implement a multi-layered approach. Here are some strategies to help you defend against email impersonation attacks:
1. Implement DMARC
DMARC otherwise known as Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance is an anti-phishing solution. It enables organizations to define procedures for addressing unauthenticated e-mails and offers a method through which people can report cases of spam and phishing.
2. Use SPF and DKIM
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework and DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail is also used to prevent email spoofing to check the sender IP address and domain that are used for sending the messages.
3. Enable Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is the extension of standard security by implementing two methods of verification for a user’s email addresses for instance through the receipt of a code through the phone.
4. Use Email Encryption
Certified, or encrypted, e-mail is useful in ensuring that messages containing sensitive information do not fall into the wrong hands since these messages are sent in coded form that only the recipient has the key to decode.
5. Develop an Email Security Policy
Design clear rules for working with emails containing confidential information, as well as the procedure for mailing suspicious messages and reacting to email spoofing.
6. Conduct Regular Security Awareness Training
Ensure that the company’s workers receive occasional training on recognising email impersonation and reporting the cases.
7. Implement Email Filtering
Work on the development of solutions for email filtering, which will help to detect and eliminate suspicious messages.
8. Monitor Email Activity
Regular scanning of emails helps in the identification of impersonation attacks and further taking the necessary measures.
9. Verify Sender Information
Check the authenticity of the sender, the email address, and the domain from where the email was sent before responding to or taking any action on the same.
10. Be Cautious of Urgent or Threatening Emails
Avoid reacting to emails that instil a sense of urgency or those that state your account or service will be cancelled if action is not taken soon.
11. Use Strong Passwords
Ensure you use challenging passwords and always avoid repeating the same password for different accounts.
12. Report Suspicious Emails
Forward such emails to the proper channel such as the human resources, Information Technology department or even the email service providers.
Best Cyber Security Practices for Individuals
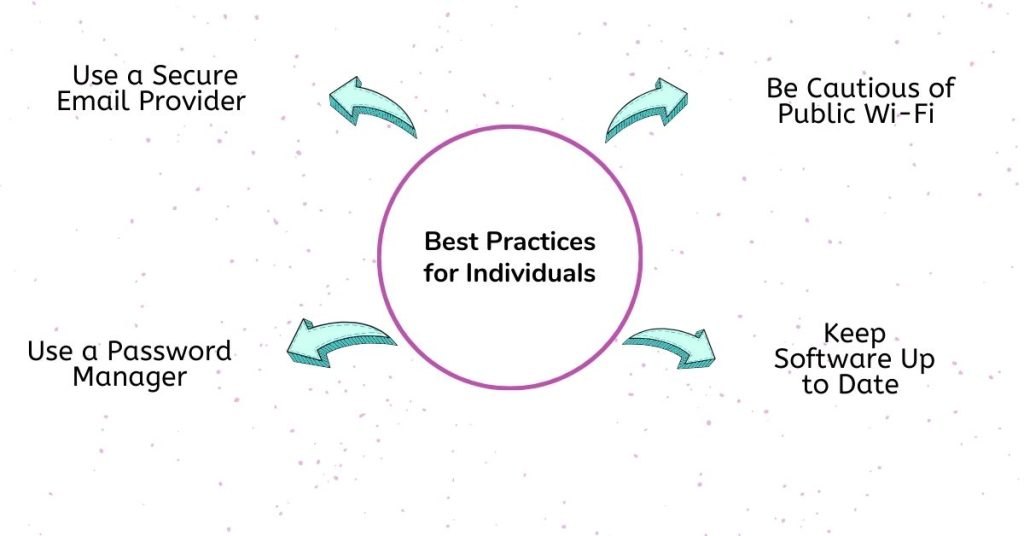
Here we bought you the best practices for individuals:
1. Use a Secure Email Provider
Go for a trusted provider who offers security aspects like mail encryption and authentication of two factors.
2. Use a Password Manager
To ensure that you have strong and different passwords for any device, use a password manager to create them for you.
3. Be Cautious of Public Wi-Fi
When connecting to the internet, should avoid using public Wi-Fi to log into personal email accounts because it is a little insecure.
4. Keep Software Up to Date
Make sure the software running on the computer such as the e-mail client, operating system etc. is the most recent containing the required safety- patches.
Best Cyber Security Practices for Organizations
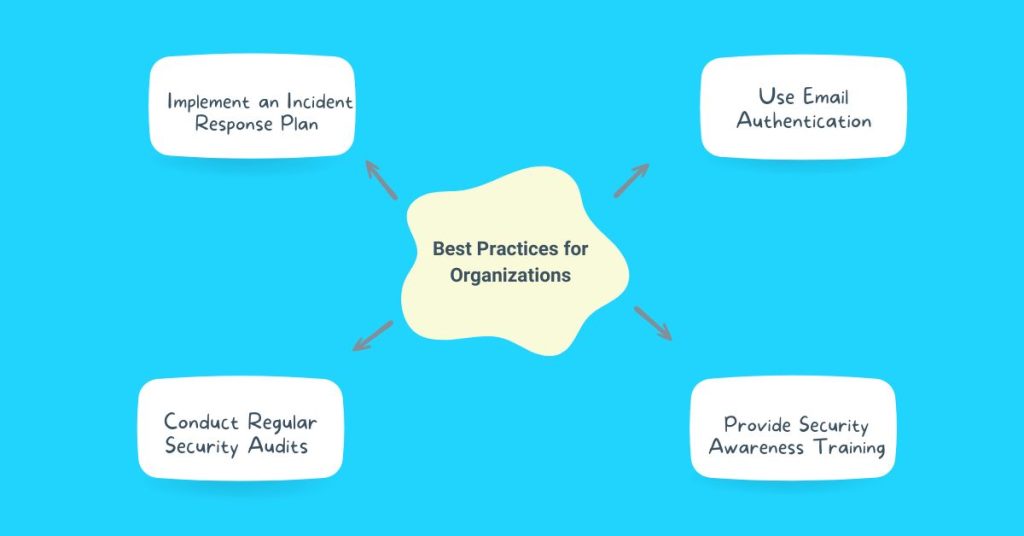
So here are the best practices for organizations:
1. Implement an Incident Response Plan
Implement an incident response plan that outlines procedures for responding to email impersonation attacks.
2. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in email systems.
3. Use Email Authentication
Use email authentication protocols, such as DMARC, SPF, and DKIM, to prevent email spoofing.
4. Provide Security Awareness Training
Provide regular security awareness training to employees on how to identify and report email impersonation attacks.
Some of the popular Phishing Emails to be aware of
Below you will find the most popular and used phishing emails by the hackers:
Example 1:
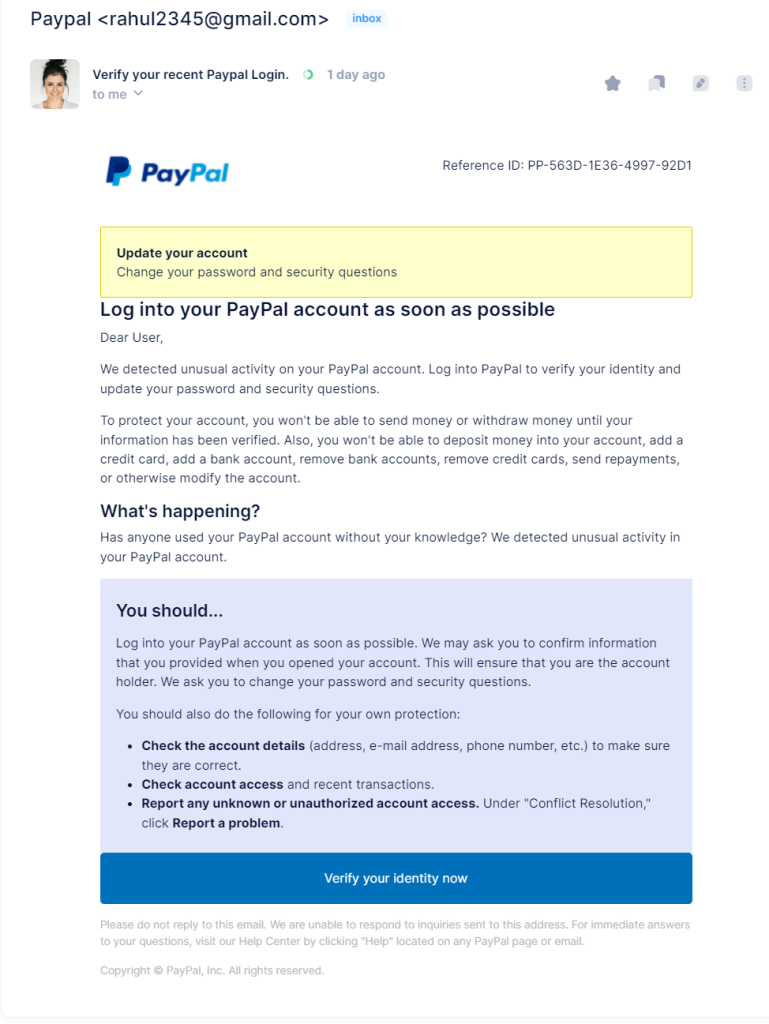
In this image, It claims that there has been unusual activity on the recipient’s account and asks them to log in to verify their identity and update their password and security questions. If you receive an email like this, it is important to be cautious and not click on any links.
Instead, you can go directly to the PayPal website by typing the address into your browser. You can also contact PayPal customer support to report the phishing email.
Example 2:
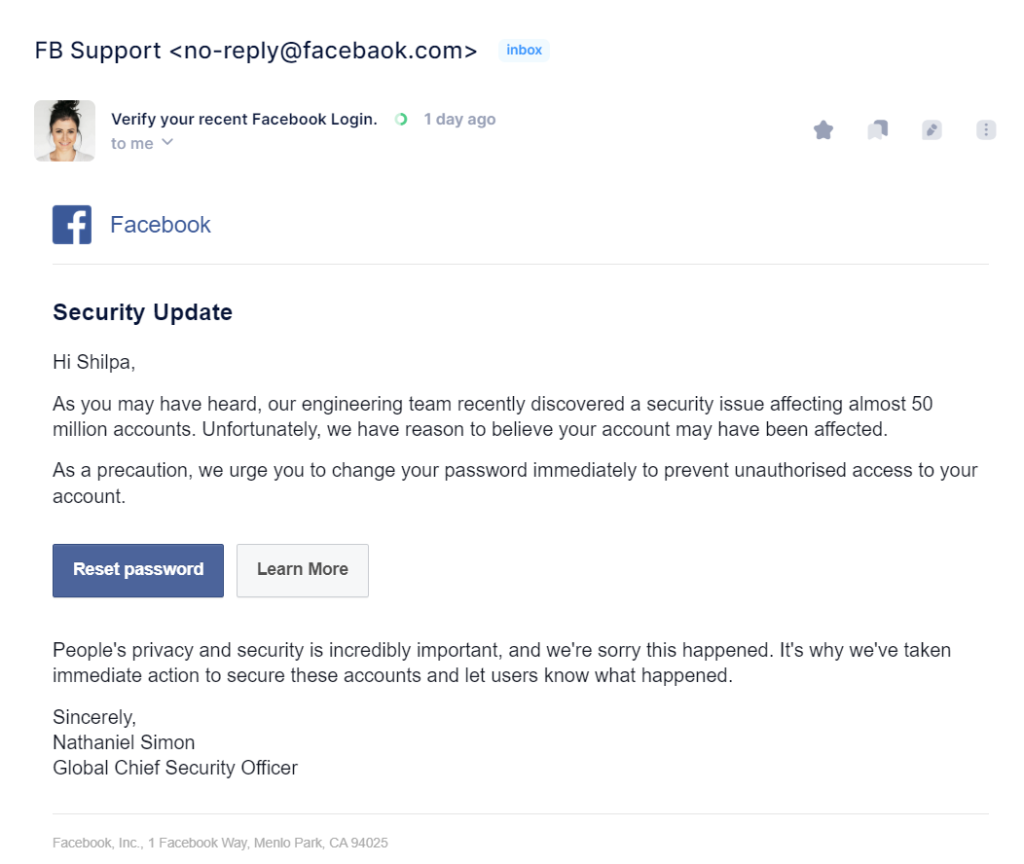
This image claims that there has been a security issue affecting almost 50 million accounts and asks the recipient to change their password immediately.
If you receive an email like this, it is important to be cautious and not click on any links. Instead, you can go directly to the Facebook website by typing the address into your browser.
You can also contact Facebook customer support to report the phishing email.
Example 3:
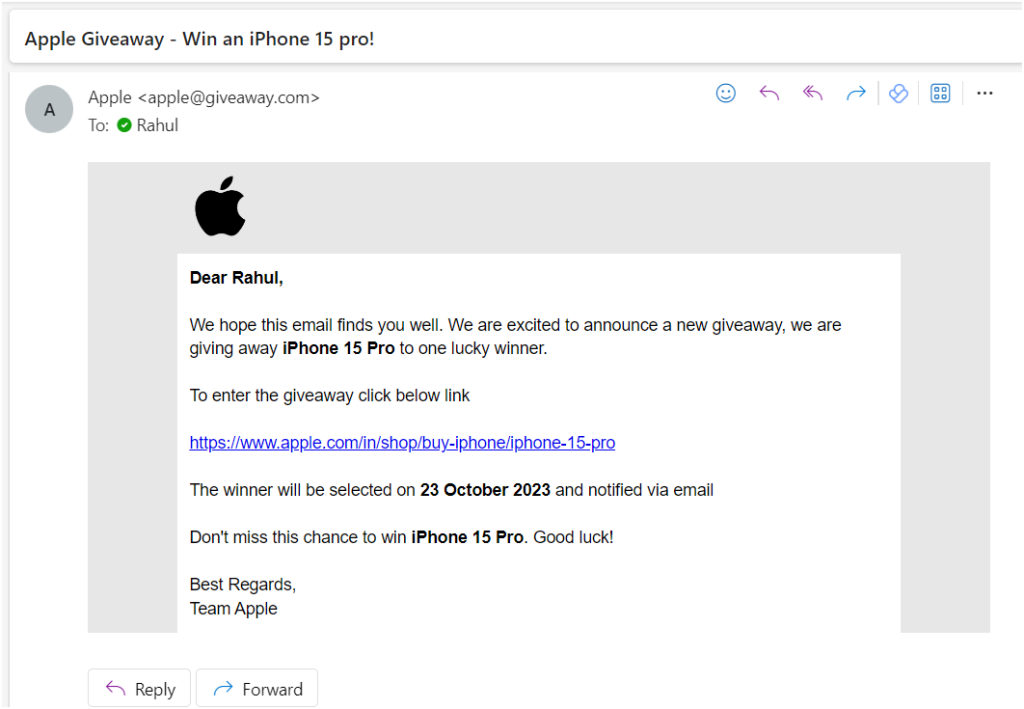
In this image, It claims that the recipient is a lucky winner of an iPhone 15 Pro and asks them to click on a link to enter the giveaway.
If you receive an email like this, it is important to be cautious and not click on any links. Instead, you can go directly to the Apple website by typing the address into your browser.
You can also contact Apple customer support to report the phishing email.
Example 4:
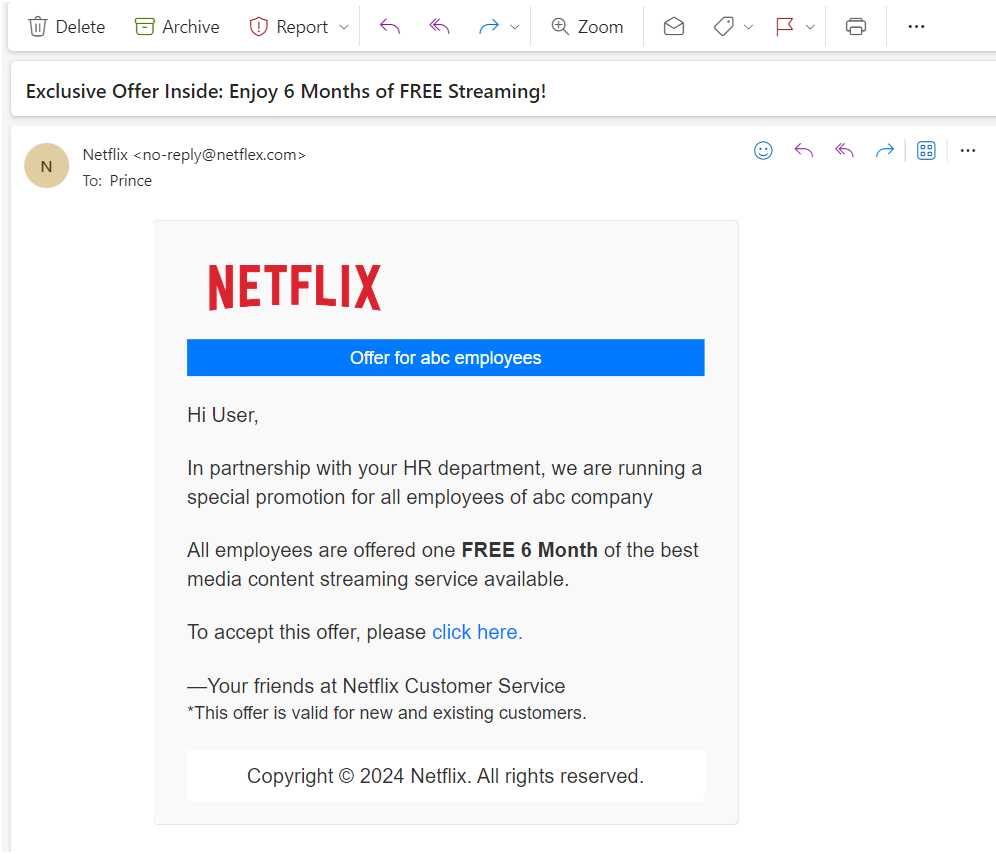
This image, claims that the recipient is eligible for 6 months of free streaming and asks them to click on a link to accept the offer.
If you receive an email like this, it is important to be cautious and not click on any links. Instead, you can go directly to the Netflix website by typing the address into your browser.
You can also contact Netflix customer support to report the phishing email.
Conclusion
Email impersonation attacks are a significant threat to individuals and organizations worldwide. To defend against these attacks, it’s essential to implement a multi-layered approach that includes technical, administrative, and behavioural controls.
By following the strategies outlined in this article, individuals and organizations can reduce the risk of falling victim to email impersonation attacks and protect sensitive information.
FAQs: How to defend against Email Impersonation Attacks? Complete Guide
1. What is an email impersonation attack?
Ans: An email impersonation attack is a type of cyber attack where an attacker sends an email that appears to come from a legitimate source, such as a colleague, business partner, or bank but is sent by the attacker to trick the recipient into divulging sensitive information or performing a certain action.
2. How do email impersonation attacks work?
Ans: Email impersonation attacks typically involve the attacker spoofing the email address of a legitimate sender, such as a CEO or colleague, and sending an email that appears to come from that sender. The email may contain malicious links, attachments, or requests for sensitive information.
3. What are the most common types of email impersonation attacks?
Ans: The most common types of email impersonation attacks include CEO scams, phishing attacks, spoofing attacks, and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.
4. How can I identify an email impersonation attack?
Ans: To identify an email impersonation attack, look for suspicious email addresses, grammatical errors, and requests for sensitive information or urgent action. Be cautious of emails that create a sense of urgency or threaten to cancel an account or service if immediate action is not taken.
5. What should I do if I receive an email impersonation attack?
Ans: If you receive an email impersonation attack, do not respond to the email or click on any links. Report the email to your IT department or email provider, and delete the email.
6. How can I prevent email impersonation attacks?
Ans: To prevent email impersonation attacks, use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and use email encryption. Be cautious of public Wi-Fi and use a secure email provider.
7. What is DMARC and how can it help prevent email impersonation attacks?
Ans: DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a protocol that helps prevent email spoofing by verifying the sender’s IP address and domain. Implementing DMARC can help prevent email impersonation attacks by blocking emails that do not authenticate properly.
8. How can I report an email impersonation attack?
Ans: Report an email impersonation attack to your IT department or email provider. You can also report the attack to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) or the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG).
9. What are the consequences of falling victim to an email impersonation attack?
Ans: Falling victim to an email impersonation attack can result in financial loss, data breaches, and reputational damage. It can also compromise sensitive information and disrupt business operations.
10. How can I educate my employees about email impersonation attacks?
Ans: Educate your employees about email impersonation attacks by providing regular security awareness training, including information on how to identify and report suspicious emails, and the importance of using strong passwords and two-factor authentication.