So, in the first part of the blog, we discussed who are the people behind these Social Engineering Attacks & what are the different types of Social Engineering attacks.
Now, in this part we would shed light on their motives, how you can identify and protect yourselves against a social engineering attack, and what are the various impacts of such attacks.
If you have not read the first part of the blog then please do so by clicking here.
Table of Contents
MOTIVES: WHY DO THEY DO IT?
The root of this question gets to the methods, thinking, and tactics used in any manipulation.
The main reasons why people choose to manipulate others can be broken down into three categories: financial, ideological and social motives.
1. Financial Motives
Financial motives are frequently the driving force behind fraud, and they are typically the most common.
Examples like lottery tickets; advertisements promoting education/careers using financial motives to lure people; receiving calls from charities for money or financial information are not unusual either.
Basically, the malicious attacker’s motive is using manipulation for his own financial gain, and therefore his motivation and his technique will reflect that.
2. Ideological Motives
Ideological motives are based on each individual’s values, principles, beliefs, ethics, and morals, which are then used to match those with people of like minds.
Some examples would be,
Political ideology:
this is where social engineers exploit one’s political ideology to raise a political issue or a controversial topic to gain access to sensitive data or systems.
Religious ideology,
where social engineers exploit one’s religious faith/values by posing as a member of a religious group to gain sensitive information
Corporate ideology
is where social engineers exploit an employee’s power or trust by convincing people to take a particular action by posing as someone in a position of authority or higher status.
3. Social Motives
Social motives are doubtlessly the most widespread and complex, especially when it comes to social engineering because they contain all other motives.
Humans are social beings by nature; it is what we do every day of our lives. The social atmosphere of a person can have a significant impact on his or her attitude toward life and self.
A few examples to explain the same,
Fear:
Fear can be used by social engineers to generate a sense of urgency and encourage people to behave in a hurry and without contemplating. For example, they may send an email alleging to be from a bank or government agency, informing victims that their account has been compromised or that they owe back taxes. The idea is to make people worry and submit personal information without first checking the request’s legitimacy.
Reciprocity
the concept of reciprocity may be used by social engineers to persuade individuals to do something for them in exchange for a minor favor. For example, they may offer a free gift or reward in exchange for taking a survey or completing a form, but the gift or reward is simply trickery to get consumers to supply personal information or do a task.
Peer Pressure
in essence, the influence of peer pressure on many people is undeniable.
Am I beautiful? Am I good enough? This behavior is particularly striking in teenagers. When social engineers discover what bothers someone, they frequently use it as a means to demand cooperation. The larger the group applying the pressure, the more likely the target will comply.
These three motives are not the only kinds that exist. They can branch out to other areas that are beyond the scope of this blog.
But the question of how you use them as a social engineer keeps evolving.
MANIPULATION TECHNIQUES

It’s not a friendly word; Manipulation is the key aspect of both social engineering and influence. It uses psychological power to influence the target’s ideology, beliefs, attitudes, and behavior.
<<WHY MANIPULATION AS A NEGATIVE PRACTICE IN SOCIAL ENGINEERING SHOULD NOT BE OVERLOOKED>>
A social engineer’s strategy would be to not inform the target that he is being controlled.
One of the goals of manipulation is to create anxiety, stress, and undue social pressure.
With that in mind, you can see why manipulation is often thought of in a negative light, but is used in social engineering and therefore must be discussed.
PERSONALITY TRAITS OF A SOCIAL ENGINEER (Behaviors/Scenarios)
Social engineering attacks center around the attacker’s use of persuasion and confidence. When exposed to these tactics, you are more likely to take actions you otherwise wouldn’t.
Now that you understand the underlying concept, you’re probably wondering “What is social engineering attack and how can I spot it?”
Among most attacks, you’ll find yourself being misled into the following behaviors:
- A Relaxing Conversation.
- Trust, belief & a great deal of confidence.
- An Unfamiliar Narrative.
- Heightened emotions, including, fear, excitement, curiosity, sadness, guilt, and anger.
- A Sense of Urgency.
- Call from a Fake IT guy.
- Anything with regards to unlocking your computer or changing passwords.
- Sharing OTP.
- Sharing your personal details.
- Donations, Charity & Fund-raisers.
- Asking you to click on unfamiliar links.
- Grammatical errors.
- Verification process by unidentifiable individuals.
By combining these tactics, the social engineer can make the victim evaluate their initial reluctance and feel pressured to disclose the information. The employee may believe that the fictional scenario is genuine and that the urgent need for information justifies their actions. This shows how social engineers can manipulate people’s thought processes to achieve their goals.
THE IMPACT: THE COST OF BEING NEGLIGENT
The impact of social engineering can go beyond lost files & stolen data. It affects a broad range spectrum, from an individual to business to society, well, not to mention, healthcare too.
Organization:
The impact of social engineering on business is tremendous. Countless companies fall victim to some form of social engineering every year.
While technology changes and grows, human nature reliably stays the same. For this reason, more and more attackers target the human part of the equation in a company’s security rather than the systems themselves. There are many different methods that attackers use to do this: baiting, quid pro quos, spear phishing, and tailgating, to name a few.
Here are some different ways that organizations can be impacted by social engineering:
- Identity theft
- Malware & ransomware attacks
- Service disruption
- Financial losses
- Data breaches
- Operational disruptions
- Productivity costs
- Unauthorized access
- Business discontinuity
Healthcare:
Social engineering can be difficult to identify, particularly in larger organizations where staff members do not always know their fellow co-workers. Attacks on healthcare can particularly have a devastating impact as they handle sensitive patient & medical data.
Some reasons social engineers target healthcare employees are:
- People are naturally trusting
- People have a desire to help
- People want to look intelligent
- People do not want to get in trouble
- Some people take shortcuts
Here are some different ways that organizations can be impacted by social engineering:
- Data breaches, including, leakage of personal information, patient data & insurance information.
- Identity thefts
- Medical frauds
- Financial losses
- Malware attacks
- Operational disruptions
- Reputational damage
- Legal actions or consequences
Individual:
Here are some different ways that organizations can be impacted by social engineering:
- Emotional harm, including, feelings of violation & embarrassment
- Reputational damage
- Identity theft; stolen social media accounts
- Financial losses
- Ransomware attacks
RECOGNIZING SOCIAL ENGINEERING TACTICS
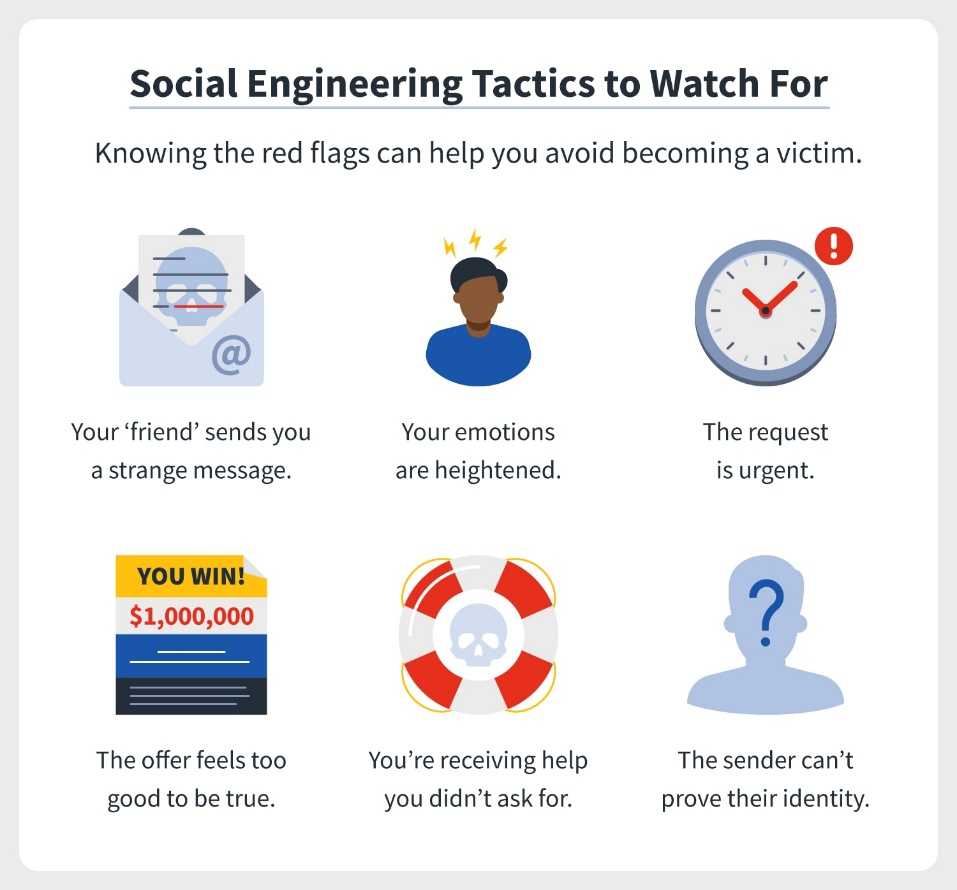
(Source: https://us.norton.com/blog/emerging-threats/what-is-social-engineering)
Recognizing social engineering tactics is an important skill to have, as it can help you avoid falling victim to scams or other malicious activities.
Here are some ways to recognize social engineering tactics:
- Be cautious of unprompted requests: Be suspicious of any communication that you did not initiate or that comes from an unknown source.
- Keep an eye out for signs of urgency or pressure: Any communication that promotes a sense of urgency, such as missed chances that require quick action, should be avoided.
- Verify identities: Verify the identity of the individual making the request through an independent source before submitting any sensitive information or cooperating with a request.
- Don’t overshare: Be cautious about sharing any personal or sensitive information, such as passwords or financial information, unless you are certain of the legitimacy of the request.
- Be cautious of offers that appear to be too good to be true: Be suspicious of any offer that appears to be too good to be true, and verify the legitimacy of the offer before taking any action.
THE RESPONSIBILITY: BECOME A HUMAN FIREWALL
This point is the epitome of everything that has been discussed so far and the guiding concept to avoiding becoming a victim.
Being ‘Responsible’ is a critical component of defending yourself or your organization from social engineering attacks. You may lessen your chances of being a victim of these malicious tactics by keeping vigilant, cautious, clever, aware, and careful.
Remember, the best defense against social engineering is a responsible and proactive approach to cybersecurity.

(Source: https://www.overtsoftware.com/human-firewall-non-technical-security-tips/)
Human Firewall; The term “human firewall” refers to a group of people in your business who offer an added line of defense against cyber-attacks.
A human firewall is a proactive approach to cybersecurity that involves training individuals to recognize and resist social engineering tactics. By increasing awareness and building knowledge about social engineering, individuals can become more confident and capable of identifying and avoiding social engineering attacks.
KEY POINTS:
- Responsibility requires vigilance: Being responsible means paying attention to your digital and physical environment. For e.g.,, if you receive an unexpected email or phone call requesting sensitive information, you can take the time to verify the legitimacy of the request before responding.
- Responsibility encourages skepticism: Being responsible means being critical of information and not taking anything at face value or something that’s too good to be true. Social engineers often rely on our natural inclination to trust others and our desire to be helpful to achieve their goals.
- Responsibility requires knowledge: Being responsible means educating yourself about the latest threats and staying informed about how to protect yourself and your organization, you can make informed decisions about how to respond to suspicious requests or situations.
- Responsibility promotes awareness: Being responsible means being aware of the risks. You can take steps to mitigate them, such as avoiding risky online behavior or implementing security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Responsibility encourages caution: Being responsible means being cautious and taking steps to minimize risk. By implementing security measures, such as using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and keeping software up to date.
AWARENESS THROUGH EDUCATION
There is no single solution, but there are ways to mitigate the ill effects of social engineering in its many forms.
<<Here are some steps to take to be educated on the prevailing social engineering attacks:>>
Keep the following points in mind to avoid getting socially engineered:
- Research & learn about social engineering.
- Train to recognize social engineering attacks
- Encourage others to adopt good cybersecurity practices, report suspicious activity, and participate in training programs.
- Response to suspicious or unexpected calls/messages or emails is to not authenticate anything or by creating distrust.
- Delete any request for financial information or passwords.
- Set your email spam filters to high.
- Secure your computing devices by installing antivirus, firewalls & keep them up to date.
- Beware of clicking random links or downloads.
- Do not plug a pen drive lying somewhere on the ground onto your computer.
- Slowdown; Attackers want you to act first and think later. So, if there’s an urgency or high pressure, don’t get influenced by it.
- Don’t open emails & attachments from unfamiliar sources. Cross-check the sender & confirm the information before initiating anything from the other end.
- Use multi-factor authentication.
- Be suspicious of tempting offers from unidentified or unknown sources.
- Never give personal or account information unless you initiated the exchange
- When a company contacts you, call them back using the phone number listed on their website. Never call them back using the phone number provided by someone you have spoken with.
- Make sure you delete all sensitive data after use even from your system’s recycle bin.
- If you are unsure about a call you received, it is wiser to leave it.
- Make sure you’re password-protecting your computer system and any external storage unit like a hard drive, disk, Pendrive, etc.
- Use a password that’s hard to guess. Don’t use the same password for all of your accounts, and don’t use something like “12345.” Make sure it’s something that would be hard to guess but easy for you to remember.
- Enable a screen locker that goes off automatically when you are away from your system.
- Don’t leave your laptop unattended in public areas.
- Don’t open email attachments from people you don’t know or trust.
- Create an information security policy for disposing of old equipment and data safely, so that it cannot be accessed or tracked down in the future by any third party.
- Make sure employees understand what they’re supposed to do with sensitive data (like passwords) when they leave the company or move on to another role.
- Ensure that your credentials are not stored in plain text on any of your servers.
- Disable all unnecessary services and protocols on your servers.
CONCLUSION:
Social engineering is still one of the most common means of cyber-attack, primarily because it is highly efficient. To criminals, the user is the ‘weakest link in the security chain’.
A door is only as secure as the person who is holding the key or the password. So, you can have the best fancy high-security system in the world, but if I manipulate you to give me the key, it’s useless.
Social engineering may be considered a bold approach to hacking because it often requires attackers to make direct contact with their targets, either by telephone or in person. At the extreme end, an attacker will physically access areas intended to be restricted to the public, such as server rooms or vaults. These audacious social engineering tactics are often dramatized by Hollywood in heist films. And, just as in the movies, social engineering in the real world requires a great deal of research and planning, as well as elaborate pretexts.
Understanding these psychological factors is essential for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By taking into account how people perceive and respond to cyber threats, we can develop better education and awareness campaigns, design more user-friendly security protocols, and create more effective policies for protecting personal and professional data.
Remember, social engineering attacks are no joke. They can be very convincing and can cause serious harm to individuals and organizations alike. So, stay vigilant, educate yourself and your team, and implement strong security measures to protect against these scams. Stay safe!
About the Author!