Cybersecurity has become a top priority for organizations across various industries. As technology advances, cyber threats also evolve, making it essential for companies to have a robust security system in place. One way to achieve this is by establishing a Security Operations Center (SOC).
In this article, we will delve into the world of SOCs, exploring what they are, their importance, and the services they provide.
What is a Security Operations Center (SOC)?
A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a centralized unit that monitors and manages an organization’s cybersecurity posture. It is a dedicated team of security professionals who work around the clock to detect, respond to, and prevent cyber threats.
A SOC is typically equipped with advanced technologies, such as threat intelligence tools, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and incident response platforms. These tools enable the SOC team to collect, analyze, and respond to security-related data from various sources across the organization.
Why is a SOC Important?

In today’s digital landscape, cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and frequent. A single breach can have devastating consequences for an organization, including financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised customer trust. A SOC helps mitigate these risks by:
1. Detecting and responding to threats in real-time
A SOC enables organizations to quickly identify and respond to cyber threats, minimizing the impact of an attack.
2. Providing continuous monitoring
A SOC operates around the clock, ensuring that an organization’s security posture is monitored continuously.
3. Enhancing incident response
A SOC has the necessary tools and expertise to respond to security incidents effectively, reducing downtime and minimizing losses.
4. Improving compliance
A SOC helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards by providing evidence of security controls and incident response capabilities.
What Services Does a SOC Provide?
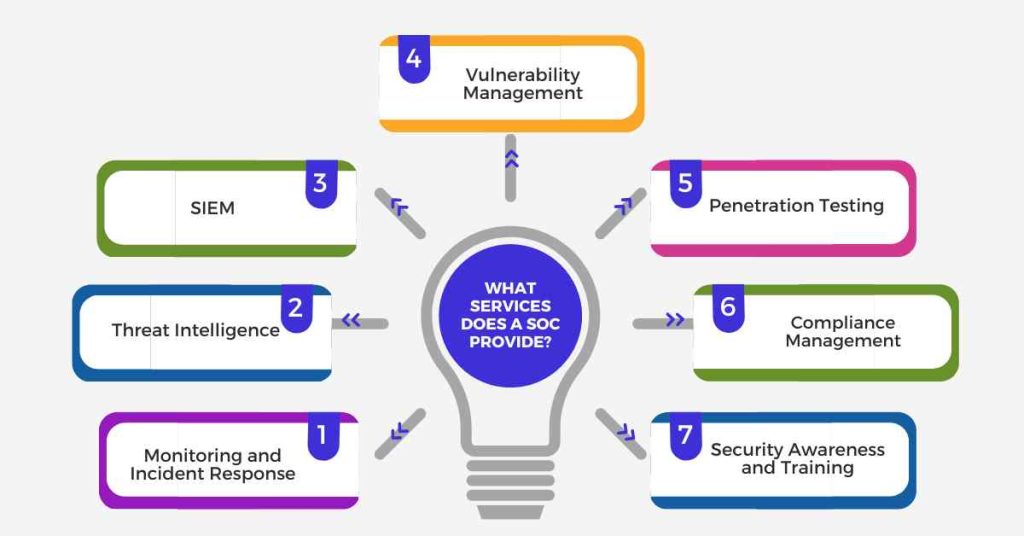
A SOC provides a range of services to help organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture. These services include:
1. Monitoring and Incident Response
A SOC continuously monitors an organization’s security-related data, detecting potential threats and responding to incidents in real-time.
2. Threat Intelligence
A SOC collects, analyzes, and disseminates threat intelligence to help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats.
3. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
A SOC uses SIEM systems to collect, store, and analyze security-related data, providing real-time visibility into an organization’s security posture.
4. Vulnerability Management
A SOC identifies and prioritizes vulnerabilities, providing recommendations for remediation and ensuring that patches are applied promptly.
5. Penetration Testing
A SOC conducts penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization’s security controls.
6. Compliance Management
A SOC helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards by providing evidence of security controls and incident response capabilities.
7. Security Awareness and Training
A SOC educates users on security best practices, phishing attacks, and other security-related topics.
Top 4 Types of SOCs
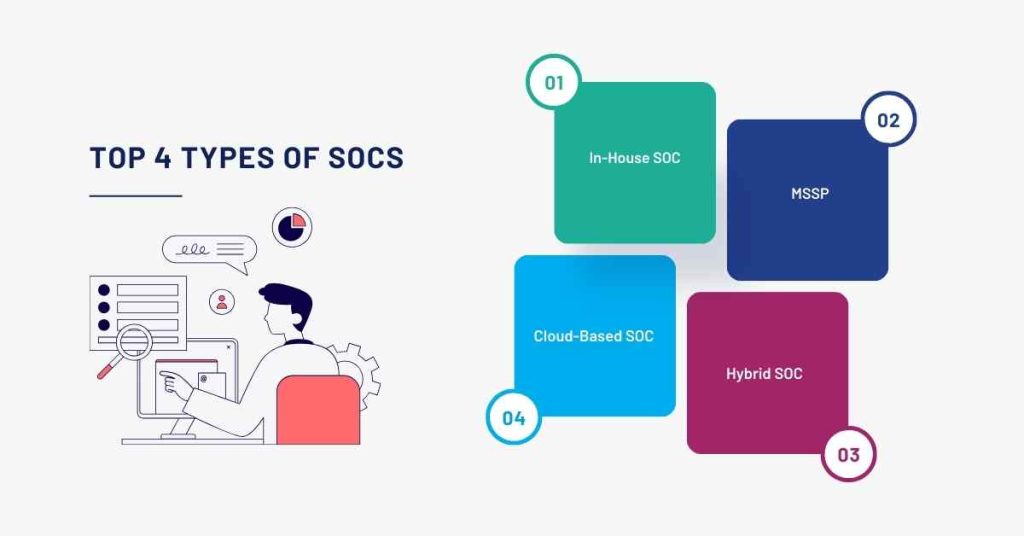
There are several types of SOCs, each with its unique characteristics and features. These include:
1. In-House SOC
An in-house SOC is a dedicated security team that operates within an organization.
2. Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP)
An MSSP is a third-party provider that offers SOC services to organizations, often leveraging cloud-based technologies.
3. Hybrid SOC
A hybrid SOC combines the benefits of an in-house SOC with the expertise of an MSSP, often using cloud-based technologies to support security operations.
4. Cloud-Based SOC
A cloud-based SOC is a virtual SOC that operates in the cloud, providing scalability and flexibility.
Top 5 Key Components of a SOC
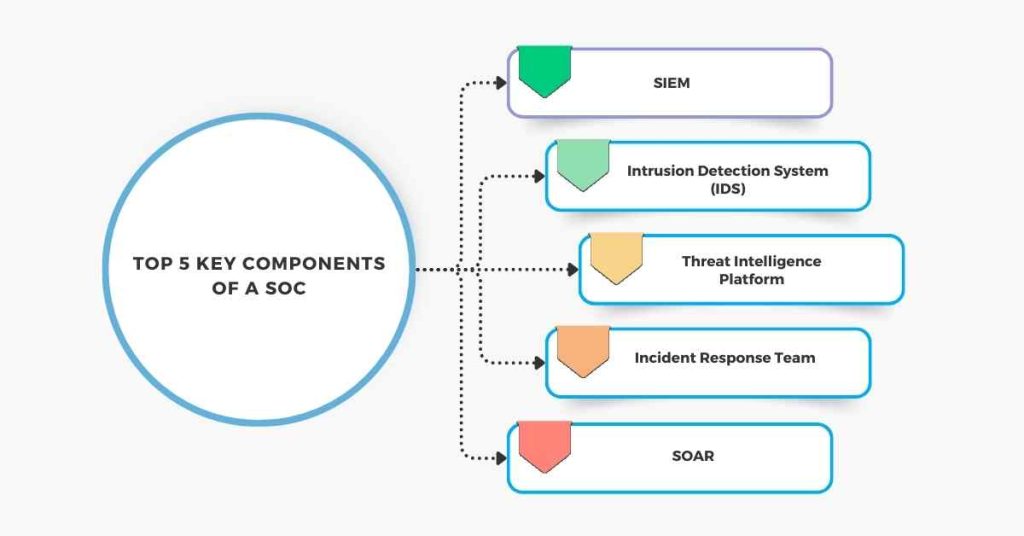
A typical Security Operations Center consists of the following key components:
1. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) System
An SIEM system is a software solution that collects and analyzes security-related data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, and applications. The SIEM system provides real-time visibility into security-related events and helps identify potential security threats.
2. Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
An IDS is a network security system that monitors and analyzes network traffic for signs of unauthorized access or malicious activity.
3. Threat Intelligence Platform
A threat intelligence platform is a software solution that collects and analyzes threat intelligence from various sources, such as public and private threat feeds, social media, and the dark web. The platform helps identify potential security threats and provides context and analysis of the threats.
4. Incident Response Team
An incident response team is a team of skilled security professionals who are responsible for responding to security incidents. The team follows a structured incident response process to contain, eradicate, and recover from security incidents.
5. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) System
A SOAR system is a software solution that automates and streamlines security incident response processes. The system helps analysts to respond to security incidents more quickly and effectively.
Top 6 Benefits of Having a SOC

Having a Security Operations Center can provide a range of benefits to organizations, including:
1. Improved Security Posture
A SOC helps organizations improve their overall security posture by providing 24/7 security monitoring, incident response, and threat-hunting services.
2. Reduced Risk
A SOC helps organizations reduce the risk of security breaches and cyber-attacks by identifying and responding to security threats in real-time.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
A SOC helps organizations meet their security compliance and regulatory requirements by providing compliance and governance services.
4. Return on Investment (ROI)
A SOC can help organizations realise a return on investment (ROI) by reducing the cost of security breaches and cyber-attacks.
5. Improved Incident Response
A SOC provides organizations with an effective incident response process to contain, eradicate, and recover from security incidents.
6. Improved Security Awareness
A SOC provides organizations with improved security awareness and education by providing training and awareness programs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a Security Operations Center is an essential component of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. A SOC provides a range of services to help organizations protect themselves against cyber threats and improve their overall security posture.
By understanding what a SOC is, its key components, and the services it provides, organizations can make informed decisions about their security needs.
FAQs: What is a Security Operations Center (SOC)?
1. What services does a SOC provide?
Ans: A SOC provides a range of services, including 24/7 security monitoring, incident response, threat hunting, penetration testing, security consulting, training and awareness, and compliance and governance.
2. How does a SOC improve an organization’s security posture?
Ans: A SOC improves an organization’s security posture by providing 24/7 security monitoring, incident response, and threat hunting services, which help to identify and respond to security threats in real-time.
3. What is the role of a SOC analyst?
Ans: A SOC analyst is a security professional who works in a Security Operations Center to monitor and analyze security-related data, identify potential security threats, and respond to security incidents.
4. What tools and technologies are used in a SOC?
Ans: A SOC uses various tools and technologies, including Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), threat intelligence platforms, and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) systems.
5. Can a SOC help with compliance and regulatory requirements?
Ans: A SOC can help organizations meet their security compliance and regulatory requirements by providing compliance and governance services, such as gap analysis and remediation.
6. How does a SOC handle incident response?
Ans: A SOC handles incident response by following a structured incident response process, which includes containment, eradication, recovery, and post-incident activities.
7. Can a SOC help with threat hunting?
Ans: A SOC can help organisations with threat hunting by using various tools and technologies to identify and respond to advanced threats.
8. How does a SOC measure its effectiveness?
A SOC measures its effectiveness by tracking metrics such as mean time to detect (MTTD), mean time to respond (MTTR), and incident response success rates, which help to assess the effectiveness of the SOC’s security operations.